Posset R, Garbade SF, Gleich F, Nagamani SCS, Gropman AL, Epp F, Ramdhouni N, Druck AC, Hoffmann GF, Kölker S, Zielonka M; Urea Cycle Disorders Consortium (UCDC) and the European registry and network for Intoxication type Metabolic Diseases (E-IMD) consortia study group. Impact of supplementation with L-citrulline/arginine after liver transplantation in individuals with Urea Cycle Disorders. Mol Genet Metab. 2024 Mar;141(3):108112. Epub 2023 Dec 10. PMID: 38301530.
L-citrulline/arginine supplementation may not improve hospital stays, growth, or brain function after liver transplants in people with urea cycle disorders (UCDs). More research is needed to determine if L-citrulline/arginine supplementation is beneficial after liver transplantation.
Key Takeaways:
- People with UCDs who receive a liver transplant are often advised to continue taking L-citrulline/arginine supplements.
- A comparison of children taking or not taking the supplements found no difference in hospitalization rates, plasma amino acid levels, growth outcomes, or neurocognitive outcomes.
- The study was limited by a small number of participants, 52 total, and missing data so its results may not be generalizable to all individuals with UCDs.
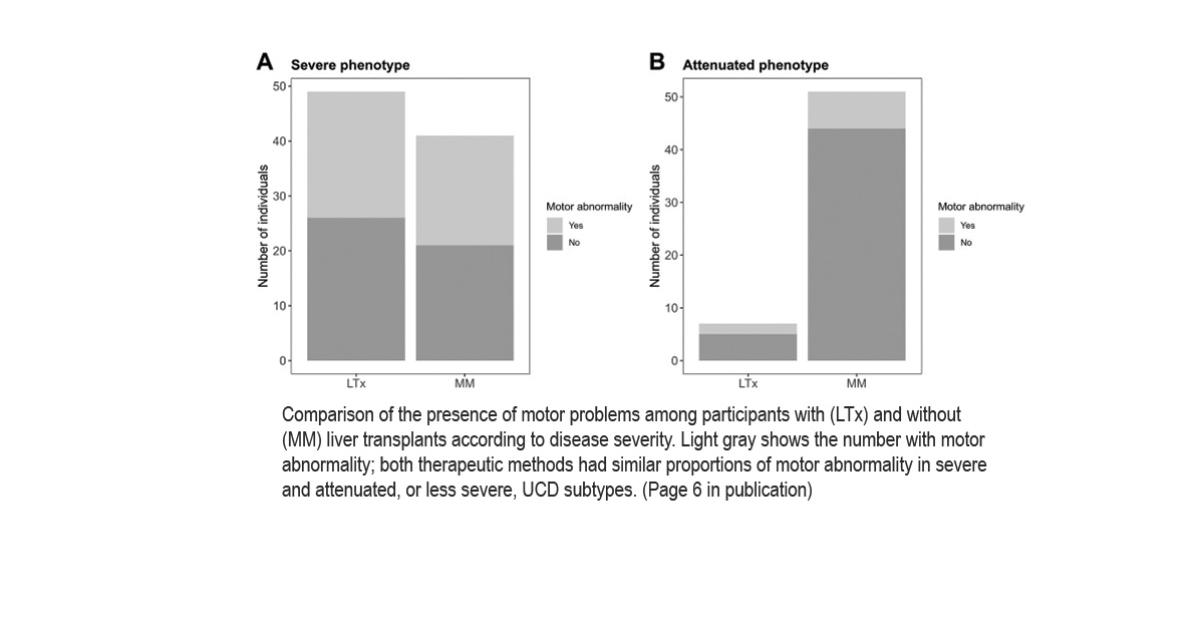
This study looked at how L-citrulline/arginine supplementation affects individuals with urea cycle disorders (UCDs) after liver transplantation (LTx). Liver transplantation is a treatment option for people with UCDs when medical treatment is not able to control hyperammonemia. L-citrulline/arginine are supplements that are typically used by most physicians when treating individuals with UCDs to prevent hyperammonemia and prevent amino acid deficiencies. However, the medical benefits of continuing L-citrulline/arginine after liver transplantation have not been thoroughly evaluated. The researchers used data collected from US, Canada, and Europe, including the Urea Cycle Disorders Consortium and the European registry and network for Intoxication type Metabolic Diseases to see if the supplementation affected hospital stays, growth, and brain function after liver transplantation.
- Hospitalization Rates After Liver Transplantation: There was no difference in the number of hospital stays between people who received the L-citrulline/arginine supplementation and those who did not, suggesting that the use of supplements did not have a strong relationship with hospital visits after surgery.
- Plasma Amino Acid Levels: The supplementation was not associated with increase in the blood levels of L-citrulline or L-arginine in the blood compared to those who did not receive the supplementation, meaning the supplements may not be effective at increasing these amino acids after transplantation.
- Growth Outcomes: Both groups showed normal growth, indicating that the supplements did not have any major effect on growth after the transplant.
- Neurocognitive Outcomes: The study did not find any improvements in neuropsychological functioning in those who took the supplements.
- Clinical Implications: L-citrulline/arginine supplementation may not improve hospital stays, growth, or brain function after a liver transplant, suggesting more research is needed to find better post-transplant care strategies.
The study had some limitations, such as a small number of participants and missing data about hyperammonemic episodes (which could affect results). Despite these limitations, the findings suggest that L-citrulline/arginine supplementation may not have a big impact on recovery after liver transplant in UCD patients.